To Accomplish This, You Can Use Either The Default-Information Originate Or The Ip Default-Network Commands.
”DEFAULT-INFORMATION ORIGINATE” COMMAND IN RIP:
Read The Following Instructions In Order To Configure The Rip Process To Send A Default Route Using The Default-Information Originate Command.
STEP 1: Enter Rip Configuration Mode.
ROUTER RIP
Step 2: Configure The Rip Process To Advertise A Default Route Out Of All Rip- Enabled Interfaces.
DEFAULT-INFORMATION ORIGINATE
THE DEFAULT-INFORMATION ORIGINATE COMMAND HAS THE FOLLOWING SYNTAX:
Default-Information Originate [Route-Map Name]
If The Route-Map Option Was Used, The Router Will Generate The Default Route If The Route Map Is Satisfied. The Route Map Allows You To Specify The Conditions That Should Be Satisfied In Order To Generate The Default Route. For Example, You Can Configure The Router To Send The Default Route If Certain Subnets Are Reachable, Or Send The Default Route Out Of Specific Interface(S) Only.
THE FOLLOWING EXAMPLE CONFIGURES THE ROUTER R1 TO ADVERTISE A RIP DEFAULT ROUTE TO BR1.
R1(Config)#Router Rip
R1(Config-Router)#Version 2
R1(Config-Router)#No Auto-Summary
R1(Config-Router)#Network 140.1.0.0
R1(Config-Router)#Network 10.0.0.0
R1(Config-Router)#Default-Information Originate
R1(Config-Router)#^Z
R1#
To Verify Our Configuration, We’ll Use The Show Ip Route Command On Br1.
R1#Show Ip Route
EXAMPLE FOR CREATING A DEFAULT ROUTE IN RIP:
You Want RIP To Propagate A Default Route.
SOLUTION:
There Are Two Ways To Get RIP To Propagate A Default Route. The Preferred Method Is Using The Default-Information Originate Command As Follows:
Router1#Configure Terminal
Enter Configuration Commands, One Per Line. End With CNTL/Z.
Router1(Config)#Ip Route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.25.1.1
Router1(Config)#Router Rip
Router1(Config-Router)#Default-Information Originate
Router1(Config-Router)#End
Router1#
IN SIMPLE SITUATIONS, YOU CAN ACCOMPLISH THE SAME THING BY JUST REDISTRIBUTING A STATIC ROUTE:
Router1#Configure Terminal
Enter Configuration Commands, One Per Line. End With CNTL/Z.
Router1(Config)#Ip Route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.25.1.1
Router1(Config)#Access-List 7 Permit 0.0.0.0
Router1(Config)#Router Rip
Router1(Config-Router)#Redistribute Static
Router1(Config-Router)#Distribute-List 7 Out Static
Router1(Config-Router)#End
Router1#
DISCUSSION:
There Are Two Main Advantages To Using Default Originate Instead Of Simply Redistributing Static Routes. The First Is That You May Have Other Static Routes On Your Router That You Do Not Want To Distribute, Or That You Want To Distribute With A Different Default Metric. In This Case, If You Just Use Redistribute Static, You Will Need To Filter Out The Unwanted Routes Using Route Maps, As Shown In, Or A Distribute-List, As We Use In This Recipe.
The Other Important Advantage Is That The Default-Information Originate Option Lets You Create A Conditional Default Route. This Means That You Can Configure The Router To Create And Distribute A Default Route Only If Some Other Route Is Present. Usually This Other Route Is A Distant Network That Indicates That The Router Is Able To See Enough Of The Outside World To Be A Reliable Default Router:
Router1#Configure Termi
”DEFAULT-INFORMATION ORIGINATE” COMMAND IN OSPF:
ENABLES OSPF DEFAULT ROUTE ORIGINATION ON THIS ROUTER.
[No] Default-Information Originate [Always] [Metric Metricval] [Metric-Type Type] [Route-Map Map-Tag]
Always: Always Advertise The Default Route Whether The Default Route Is Present Or Not In The Routing Table. If Used With The No Form Of The Command, The Default Route Will Be Originated Only When The Default Route Is Present In The Routing Table. Default Value: Disabled.
Metricval: Metric Used For Generating The Default Route. If The No Form Of The Command Is Used With The Metric Keyword, The Default Metric Value Is Restored. Valid Values: 0 - 4294967295. Default Value: 10
Type: External Link Type Associated With The Default Route. If The No Form Of The Command Is Used With The Metric-Type Keyword, The Default Metric Type Is Restored. Valid Values: 1 = Type 1 External Route Or 2 = Type 2 External Route. Default Value: 2.
Map-Tag: Specifies The Route-Map Name Containing The Criteria That Must Be Satisfied For The Default Route To Be Generated. Default Value: No Route-Map Specified.
Description: Ospf Default Route Origination Enables The Router To Generate Default Route Advertisement (0/0) In Its External Lsa. It Generates A Default Route If Manually Configured Default Route Exists Or The Always Keyword Is Specified."
If The Router Receives An Lsa With The Default Route, It Will Install The Default Route Based Upon A Metric Criterion If Multiple Default Route Entries Exist. In The Event Of A Default Route Being Redistributed From Other Routing Protocols, Default Route Origination Will Take The Precedence And Replace The Export Entry.
Use The Default-Information Originate Command To Enable Default Route Origination On This Router. A Default Route Will Only Be Generated If A Default Route Has Been Manually Configured.
Use The Default-Information Originate Always Command To Always Generate A Default Route Into The Ospf Domain.
Use The Default-Information Originate Metric Command To Specify A Metric Used When Generating The Default Route. If The Metric Is Also Set In The Set Clause Of The Route-Map Specified Using The Route-Map Keyword, The Metric Corresponding To The Route-Map Will Be Used.
USE THE DEFAULT-INFORMATION ORIGINATE METRIC-TYPE COMMAND:
Use The No Default-Information Originate Command To Disable Default Route Origination On This Router. Specifying Any Option With The No Command Only Changes The Option To Its Default Value Leaving The Remainder Of The Configuration Unchanged.
Factory Default: Disabled
COMMAND MODE: ROUTER OSPF
Example 1:
The Following Example Forces The Generation Of A Default Route Into The Ospf Domain If The Metric And Route-Map Criteria Are Met And A Default Route Is Configured:
Router#Configure Terminal
Enter Configuration Commands, One Per Line. End With Cntl/Z.
Router(Config)#Router Ospf 1
Router(Config-Router)#Default-Information Originate Metric 50 Metric-Type 1 Route-Map R1
Router(Config-Router)#Show
!.
Router Ospf 1
Default-Information Originate Metric 50 Metric-Type 1 Route-Map R1
!
Example 2:
The Following Example Removes The Route Map Configured In Example 1 From The Default Route Origination Configuration:
Router#Configure Terminal
Enter Configuration Commands, One Per Line. End With Cntl/Z.
Router(Config)#Router Ospf 1
Router(Config-Router)#No Default-Information Originate Route-Map R1
Router(Config-Router)#Show
!
Router Ospf 1
Default-Information Originate Metric 50 Metric-Type 1
!
Example 3:
The Following Example Removes The Default Route Origination Configuration For This Router:
Router#Configure Terminal
Enter Configuration Commands, One Per Line. End With Cntl/Z.
Router(Config)#Router Ospf 1
Router(Config-Router)#No Default-Information Originate
Router(Config-Router)#Show
!
Router Ospf 1
!
Related Commands: Router Ospf
Show
Show Ospf
Show Running-Config Ospf
THERE ARE MANY WAYS OF SENDING A DEFAULT ROUTE IN OSPF.SAME ARE HERE:
Always Keyword
EASIEST WAY IS WITH THE ALWAYS KEYWORD.
R2(Config-If)#Router Os 1
R2(Config-Router)#Default-Information Originate Always
No Matter What This Router Will Always Originate The Default Route Regard Less If It Knows Of One Or Not.
STUB / TOTALLY STUBBY AREA
This Will Generate A Default Route In To An Area
R2(Config)#Router Os 1
R2(Config-Router)#Area 1 Stub
Or
R2(Config-Router)#Area 1 Stub No-Summary
NSSA AREA (TYPE 7 DEFAULT AND TYPE 3 DEFAULT)
Not To Be Left Out Nssa Area Can Also Inject Defaults Into Their Areas. Nssa Area Have The Option Of A Type 7 Route (N2) Or A Type 3 (Ia)
TYPE 7
R3(Config)#Router Os 1
R3(Config-Router)#Area 2 Nssa Default-Information-Originate
TYPE 3
R3(Config)#Router Os 1
R3(Config-Router)#Area 2 Nssa No-Summary
CONDITIONAL ADVERTISEMENT – WHEN EITHER OF 2 ROUTES EXIST
1) Create An Access-List To Match The Two Routes
R2(Config)#Access-List 10 Permit Host 33.0.0.0
R2(Config)#Access-List 10 Permit Host 44.4.4.4
2) Create A Route-Map To Match Them
R2(Config)#Route-Map Default
R2(Config-Route-Map)#Match Ip Add 10
3) Under The Ospf Process Set To The Route-Map On The Default-Information Originate Command
R2(Config-Route-Map)#Router Os 1
R2(Config-Router)#Default-Information Originate Route-Map Default
IF EITHER ROUTE IS UP THEN THE DEFAULT IS GENERATED.
CONDITIONAL ADVERTISEMENT – WHEN 2 ROUTES EXIST
1) Create A Track For The 2 Routes
R2(Config)#Track 1 Ip Route 33.0.0.0/8 Reachability
R2(Config)#Track 2 Ip Route 44.4.4.4/32 Reachability
2) Create A Track List To Track Both Routes. Here We Can Use The “No” Or “Or” Operators To Provide For More Complex Logic.
R2(Config)#Track 3 List Boolean And
R2(Config-Track)#Object 1
R2(Config-Track)#Object 2
R2(Config-Track)#Ex
TWO DIFFERENT OPTIONS HERE, ONE USE A DEFAULT ROUTE TO TRACK OR TWO ANOTHER NETWORK TO TRACK.
3) (Option 1) Default Route
R2(Config)#Ip Route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Null 0 Track 3
R2(Config)#
R2(Config)#Router Os 1
R2(Config-Router)#Default-Information Originate
Based On The Two Routes Being Available The Default Route Will Appear In The Table And Then Ospf Will Start Originating It.
3) (Option 2) Match Another Network
R2(Config)#Ip Route 200.200.200.200 255.255.255.255 Null 0 Track 3
R2(Config)#Ip Prefix-List Match200 Permit 200.200.200.200/32
R2(Config)#
R2(Config)#Route-Map Rm-Match200
R2(Config-Route-Map)#Match Ip Add Pref Match200
R2(Config-Route-Map)#
R2(Config-Route-Map)#
R2(Config-Route-Map)#Router Os 1
R2(Config-Router)#Default-Information Originate Route-Map Rm-Match200
The Track Is Added To A Dummy Route 200.200.200.200/32 Which Is Then Match By The Prefix List In The Route-Map Which Then Triggers The Default To Be Sent By Ospf.
HOW OSPF INJECTS A DEFAULT ROUTE INTO A NORMAL AREA:
The OSPF Router Does Not, By Default, Generate A Default Route Into The OSPF Domain. In Order For OSPF To Generate A Default Route, You Must Use The Default-Information Originate Command.
There Are Two Ways To Advertise A Default Route Into A Normal Area. The First Is To Advertise 0.0.0.0 Into The OSPF Domain, Provided The Advertising Router Already Has A Default Route. The Second Is To Advertise 0.0.0.0 Regardless Of Whether The Advertising Router Already Has A Default Route. The Second Method Can Be Accomplished By Adding The Keyword Always To The Default-Information Originate Command.
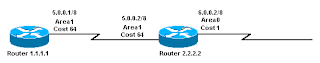
The Configurations Shown Here:
Router 1.1.1.1:
Current configuration:
hostname r1.1.1.1
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0
interface Serial2/1/0
ip address 5.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
router ospf 2
network 5.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 1
end
Router 2.2.2.2:
Current configuration:
hostname r2.2.2.2
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.0.0.0
interface Serial0/1/0
ip address 5.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
interface ATM1/0.20
ip address 6.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
router ospf 2
network 5.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 1
network 6.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
default-information originate
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 6.0.0.3
end
VERIFY:
This Section Provides Information You Can Use To Confirm Your Configuration Is Working Properly.
Show Ip Ospf Database—Displays A List Of The Link State Advertisements (Lsas) And Types Them Into A Link State Database. This List Shows Only The Information In The LSA Header.
Show Ip Ospf Database External—Displays Information Only About The External Lsas.
Show Ip Route—Displays The Current Status Of The Routing Table.
EXAMINE THE OSPF DATABASE
This Output Displays How The OSPF Database Looks Given This Network Environment, Using The Show Ip Ospf Database Command.
R2.2.2.2#Show Ip Ospf Database
CONCLUSION:
The Goal Of This Article Is To Give An Easy Way To Understand The Cisco – Basic Configuring Of “DEFAULT-INFORMATION ORIGINATE” COMMAND, Hope This Article Will Helps Every One (Beginners) Who Are Going To Start Cisco Lab Practice Without Any Doubts. Thank You!
This Article Written Author By: Premakumar Thevathasan. CCNA, CCNP, CCIP, MCSE, MCSA, MCSA - MSG, CIW Security Analyst, CompTIA Certified A+.
DISCLAIMER:
This Document Carries No Explicit Or Implied Warranty. Nor Is There Any Guarantee That The Information Contained In This Document Is Accurate. Every Effort Has Been Made To Make All Articles As Complete And As Accurate As Possible.
It Is Offered In The Hopes Of Helping Others, But You Use It At Your Own Risk. The Author Will Not Be Liable For Any Special, Incidental, Consequential Or Indirect Any Damages Due To Loss Of Data Or Any Other Reason That Occur As A Result Of Using This Document. But No Warranty Or Fitness Is Implied. The Information Provided Is On An "As Is" Basic. All Use Is Completely At Your Own Risk.
For More - > Http://Www.Cisco.Com/En/Us/Docs/Ios/12_3t/Ip_Route/Command/Reference/Ip2_C1gt.Pdf
The School Of Cisco Networking (SCN)

2 comments:
We are very very Grateful you sir.I would like to extend my heartfelt thanks to you Mr.Premakumar Thevathasan sir.
Your Teaching is Rooking.Thank you for teaching us, from bottom of our heart...
This is So quit of learning site(THE SCHOOL OF CISCO NETWORKING).I feel I motivated by your teaching.
Sir your teaching is an amazing.Thank you sir.
best regards - Boong Lee.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_3t/ip_route/command/reference/ip2_c1gt.html#wp1094086
Post a Comment